Credential providers today heavily depend on technology and data in virtually every aspect of their operations. The integration of credential information across different systems is not simply a technical challenge but a critical measure for creating a more efficient and supportive educational framework that boosts student success. For individuals acquainted with the post-secondary education system, navigating administrative requirements might seem like a routine part of the academic experience. However, for many, these requirements — from exploring credential options and applying for programs to securing financial aid, registering for courses, scheduling advisor meetings, locating resources, and planning for graduation — can represent significant hurdles. Complexities introduced by IT systems can further complicate these processes, becoming an impediment rather than an aid. Well-integrated credential management systems support end-to-end workflows for multiple credentials operations, from designing and developing the credential to verifying issuance of individual credentials and supporting post-graduation pathways.
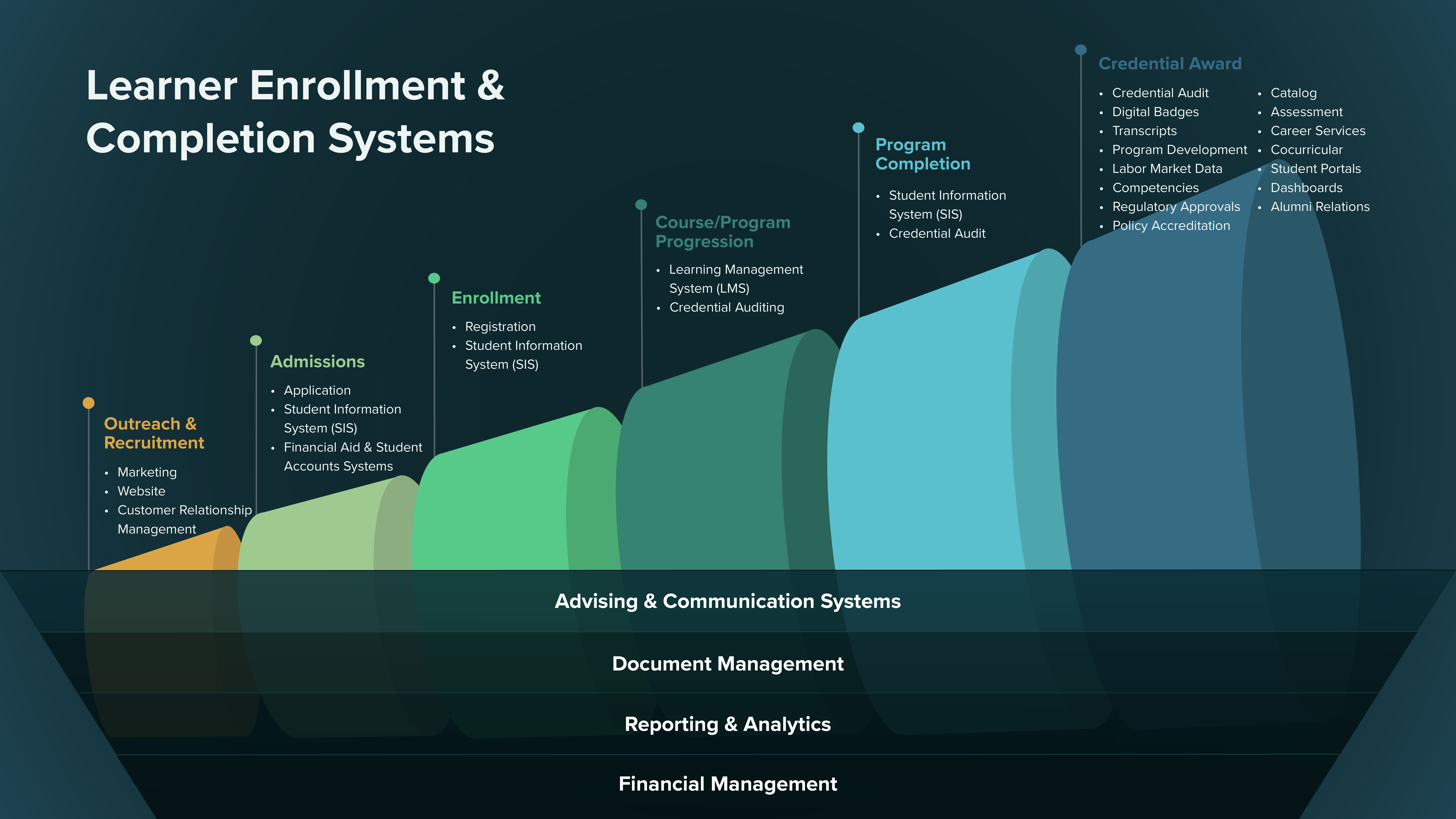
The "End-to-End Credential Workflow Supports" diagram illustrates key phases where well integrated credential management systems are vital, such as,
Managing the full suite of technologies used by an organization for handling credential information can be a challenge. With most credential-issuing bodies now employing a variety of tools and systems, credential data can be created, stored, and updated across multiple tools and systems. This dispersion of data can make even the generation of basic reports a complex and labor-intensive task. For instance, a course catalog tool that contains details on program-level learning outcomes, may not seamlessly connect with the student-level achievement data residing in an assessment tool.
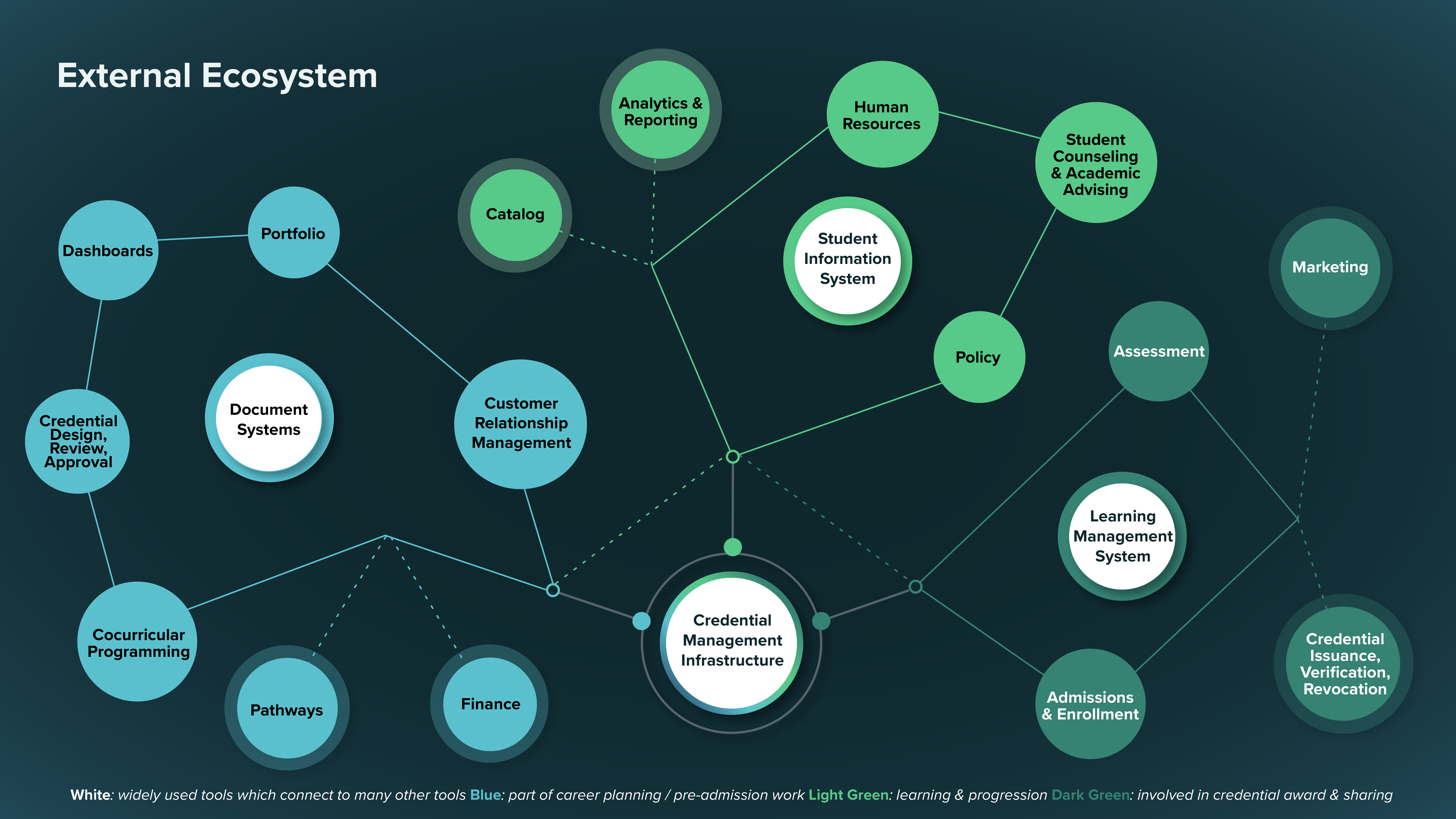
*White: widely used tools which connect to many other tools Blue: part of career planning / pre-admission work Light Green: learning & progression Dark Green: involved in credential award & sharing
The Conceptual Credential Architecture diagram outlines some of the prevalent tools and integrations that are instrumental for the storage and management of credential information, such as:
Integrated credential IT systems are crucial for institutions aiming to offer innovative credential offerings at scale. This strategic resource empowers institutions to select applications that are best suited to their specific operational demands and the needs of their users. Nonetheless, the autonomy to choose comes with its own set of challenges, particularly when different applications lack the capacity for smooth data exchange. Although the adoption of data standards has alleviated some interoperability issues, institutions continue to grapple with the challenge of configuring their IT infrastructures to support their distinctive needs comprehensively. With the credentialing ecosystem expanding to incorporate new forms of credentials like microcredentials, the complexity of managing such diverse information multiplies. Institutions capable of orchestrating the widespread distribution of credential information across an array of systems are well positioned to respond to emerging workforce needs.
This technology playbook, Integrated Credential Management, focuses on how to create, share, and update credential information across an institution to maintain flexibility at the department level while effectively managing widely used data across the organization. This playbook addresses these challenges by showcasing case studies of institutions that have successfully developed IT and business solutions capable of integrating the necessary information across diverse systems and applications. It serves as a valuable resource for institutions seeking to optimize their credential management processes, enhance data consistency, and leverage technology to meet the evolving needs and expectations of stakeholders within the credentialing ecosystem.

Credential As You Go has acquired three phases of funding to date. Lumina Foundation funded Phase I, resulting in the Incremental Credential Framework for testing. The Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education funds Phase II (Grant R305T210063), which focuses on rapid prototyping of and research on incremental credentials with a national campaign. An anonymous private donor fund at the Program on Skills, Credentials & Workforce Policy at George Washington University funds the development of the prototype Learn and Work Ecosystem Library. Walmart funds Phase III, which focuses on systems change for expansion and sustainability of incremental credentials. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of Lumina Foundation, Institute of Education Sciences, the U.S. Department of Education, Walmart, or George Washington University.